Smart Car OTA Updates and Emergency Access
A pregnant woman in Shandong, China faced a critical situation when her car required a 51-minute system update just as she needed to go to the hospital for delivery, sparking discussion about smart vehicle design and user safety.
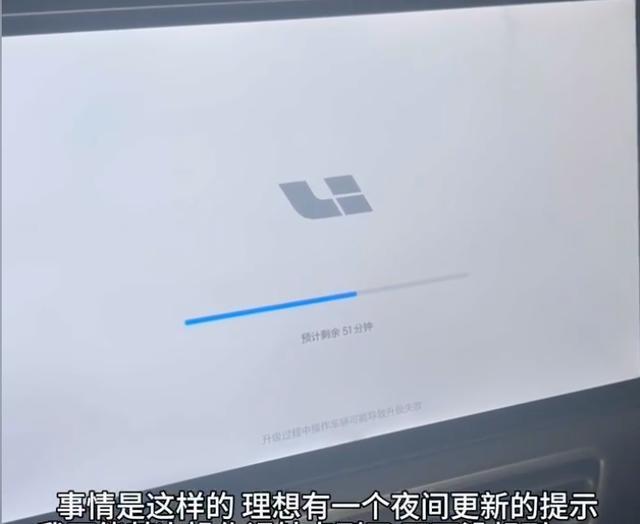
The intersection of automotive technology and emergency situations has become a pressing concern as demonstrated by a recent incident in Shandong, China. A pregnant woman found herself in a challenging position when her Ideal (Li Auto) vehicle initiated a system update that would render the car inoperable for 51 minutes, precisely when she needed to reach the aspects of modern vehicle design. Smart cars increasingly rely on over-the-air (OTA) updates to maintain and improve their systems. While these updates are essential for vehicle functionality and safety, their implementation raises important questions about user access and control.
Industry experts and automotive engineers point out that vehicle software architecture should maintain a clear separation between critical driving functions and auxiliary features. The fundamental ability to operate a vehicle should never be compromised by software updates. This principle is particularly crucial for emergency situations where immediate vehicle access could be life-critical.
The technical community suggests several potential solutions, drawing from industrial control systems where redundancy is standard practice. These include implementing A/B system partitioning, allowing for rollback capabilities, and maintaining essential driving functions separate from entertainment and comfort features.
Consumer advocates emphasize that while software updates are necessary for modern vehicles, manufacturers must prioritize user safety and accessibility. They suggest implementing better timing controls, emergency override options, and clearer communication about update requirements and duration.
The incident has prompted broader discussions about the balance between technological advancement and practical safety concerns in modern vehicles. It also raises questions about the responsibility of automotive manufacturers to ensure their vehicles remain accessible during critical situations, regardless of software update status.
This case serves as a catalyst for the automotive industry to reconsider how they implement system updates, potentially leading to improved protocols that better serve both technological needs and human safety requirements.