China's Aggressive Fiscal Policy and Monetary Easing in 2025: Economic Implications
China’s Central Financial Work Conference signals a major policy shift for 2025, implementing more aggressive fiscal measures and transitioning from ‘prudent’ to ‘appropriately loose’ monetary policy with potential interest rate cuts.
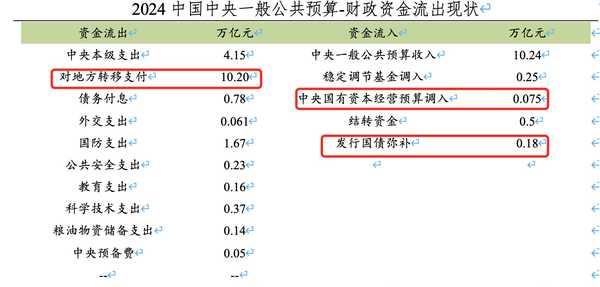
The recent Central Economic Work Conference in China has set the stage for significant policy changes in 2025, marking a decisive shift in the country’s economic strategy. This comprehensive policy adjustment reflects China’s determination to address both immediate challenges and long-term development goals.
The fiscal policy transformation represents the first major shift in China’s approach since 2010. The government plans to increase its fiscal deficit ratio above 4%, significantly higher than previous years. This expansion will be supported by issuing ultra-long-term special treasury bonds and local government special bonds, with a total scale potentially reaching 2-3 trillion yuan.
The monetary policy transition is equally significant. After maintaining a “prudent” monetary stance for 14 years, China’s central bank will adopt an “appropriately loose” approach. This shift is expected to include:
- Multiple rounds of interest rate cuts throughout 2025
- Reduction in both reserve requirement ratio and lending rates
- Expanded liquidity support through various monetary tools
- Innovation in financial instruments to maintain market stability
The impact on daily life will manifest through several channels. In the real estate sector, mortgage rates are likely to decrease further, potentially stimulating housing market activity. For consumers, while immediate inflation pressure remains limited due to current economic conditions, the policy shift aims to gradually boost consumption confidence and household income.
For financial markets, the policy adjustment is expected to benefit both bond and equity markets. The increased fiscal deficit and monetary easing should provide substantial liquidity support, though the transmission effect may take time to materialize in the real economy.
The government also emphasizes supporting key strategic industries, particularly in technology and innovation. This includes major investments in artificial intelligence, new infrastructure, and other emerging sectors that could create new employment opportunities and economic growth points.
This policy combination signals China’s commitment to balancing short-term stability with long-term development goals. While the immediate effects may not be dramatic, the cumulative impact of these measures is expected to gradually strengthen economic momentum and improve public confidence in China’s economic prospects.
The success of these policies will largely depend on their implementation and the global economic environment in 2025. The government has acknowledged external challenges and domestic complexities, demonstrating a more pragmatic approach to economic management while maintaining ambitious development goals.